Google Cloud Certified - Professional Cloud Network Engineer
Last Update 2 months ago
Total Questions : 215
Google Cloud Certified - Professional Cloud Network Engineer is stable now with all latest exam questions are added 2 months ago. Incorporating Professional-Cloud-Network-Engineer practice exam questions into your study plan is more than just a preparation strategy.
Professional-Cloud-Network-Engineer exam questions often include scenarios and problem-solving exercises that mirror real-world challenges. Working through Professional-Cloud-Network-Engineer dumps allows you to practice pacing yourself, ensuring that you can complete all Google Cloud Certified - Professional Cloud Network Engineer practice test within the allotted time frame.
You work for a university that is migrating to Google Cloud.
These are the cloud requirements:
On-premises connectivity with 10 Gbps
Lowest latency access to the cloud
Centralized Networking Administration Team
New departments are asking for on-premises connectivity to their projects. You want to deploy the most cost-efficient interconnect solution for connecting the campus to Google Cloud.
What should you do?
Question:
Your organization has distributed geographic applications with significant data volumes. You need to create a design that exposes the HTTPS workloads globally and keeps traffic costs to a minimum. What should you do?
You have configured a Compute Engine virtual machine instance as a NAT gateway. You execute the following command:
gcloud compute routes create no-ip-internet-route \
--network custom-network1 \
--destination-range 0.0.0.0/0 \
--next-hop instance nat-gateway \
--next-hop instance-zone us-central1-a \
--tags no-ip --priority 800
You want existing instances to use the new NAT gateway. Which command should you execute?
Your company has separate Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) networks in a single region for two departments: Sales and Finance. The Sales department's VPC network already has connectivity to on-premises locations using HA VPN, and you have confirmed that the subnet ranges do not overlap. You plan to peer both VPC networks to use the same HA tunnels for on-premises connectivity, while providing internet connectivity for the Google Cloud workloads through Cloud NAT. Internet access from the on-premises locations should not flow through Google Cloud. You need to propagate all routes between the Finance department and on-premises locations. What should you do?
Your end users are located in close proximity to us-east1 and europe-west1. Their workloads need to communicate with each other. You want to minimize cost and increase network efficiency.
How should you design this topology?
You are disabling DNSSEC for one of your Cloud DNS-managed zones. You removed the DS records from your zone file, waited for them to expire from the cache, and disabled DNSSEC for the zone. You receive reports that DNSSEC validating resolves are unable to resolve names in your zone.
What should you do?
You have the following Shared VPC design VPC Flow Logs is configured for Subnet-1 In the host VP
C.
You also want to monitor flow logs for Subnet-2. What should you do?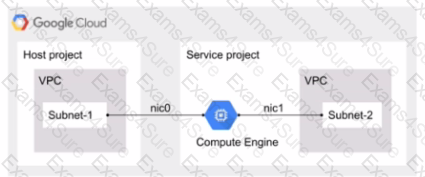
You are designing a Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) cluster for your organization. The current cluster size is expected to host 10 nodes, with 20 Pods per node and 150 services. Because of the migration of new services over the next 2 years, there is a planned growth for 100 nodes, 200 Pods per node, and 1500 services. You want to use VPC-native clusters with alias IP ranges, while minimizing address consumption.
How should you design this topology?
You have deployed a proof-of-concept application by manually placing instances in a single Compute Engine zone. You are now moving the application to production, so you need to increase your application availability and ensure it can autoscale.
How should you provision your instances?
You are the network administrator responsible for hybrid connectivity at your organization. Your developer team wants to use Cloud SQL in the us-west1 region in your Shared VP
C.
You configured a Dedicated Interconnect connection and a Cloud Router in us-west1, and the connectivity between your Shared VPC and on-premises data center is working as expected. You just created the private services access connection required for Cloud SQL using the reserved IP address range and default settings. However, your developers cannot access the Cloud SQL instance from on-premises. You want to resolve the issue. What should you do?

TESTED 04 Apr 2025
Hi this is Romona Kearns from Holland and I would like to tell you that I passed my exam with the use of exams4sure dumps. I got same questions in my exam that I prepared from your test engine software. I will recommend your site to all my friends for sure.
Our all material is important and it will be handy for you. If you have short time for exam so, we are sure with the use of it you will pass it easily with good marks. If you will not pass so, you could feel free to claim your refund. We will give 100% money back guarantee if our customers will not satisfy with our products.