QMS ISO 9001:2015 Lead Auditor Exam
Last Update 4 days ago
Total Questions : 210
QMS ISO 9001:2015 Lead Auditor Exam is stable now with all latest exam questions are added 4 days ago. Incorporating ISO-9001-Lead-Auditor practice exam questions into your study plan is more than just a preparation strategy.
ISO-9001-Lead-Auditor exam questions often include scenarios and problem-solving exercises that mirror real-world challenges. Working through ISO-9001-Lead-Auditor dumps allows you to practice pacing yourself, ensuring that you can complete all QMS ISO 9001:2015 Lead Auditor Exam practice test within the allotted time frame.
In the context of a third-party audit, match the event with the responsibility for conducting it.

You are carrying out an audit at a single-site organisation seeking certification to ISO 9001 for the first time. The organization manufactures cosmetics for major retailers.
You are interviewing the Manufacturing Manager (MM).
You: "I would like to begin by looking at the cleaning controls."
MM: "We record the cleaning of the equipment at the end of every batch. This document details the minimum cleaning frequency and the procedures to follow for all areas and each item of equipment. The person who carries out the cleaning puts their initial on the document and records the time and date alongside."
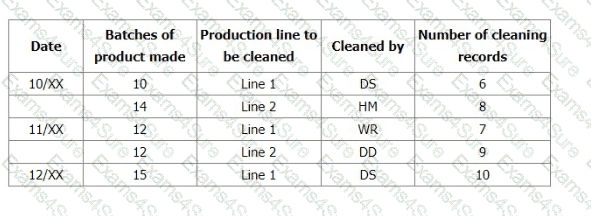
Narrative: You sample production records over 3-days and note down evidence of nonconformity as per the table below.
Scenario 5: Mechanical-Electro (ME) Audit Stages
Mechanical-Electro, better known as ME, is an American company that provides mechanical and electrical services in China. Their services range from air-conditioning systems, ventilation systems, plumbing, to installation of electrical equipment in automobile plants, electronic manufacturing facilities, and food processing plants.
Due to the fierce competition from local Chinese companies and failing to meet customer requirements, ME's revenue dropped significantly. In addition, customers' trust and confidence in the company decreased, and the reputation of the company was damaged.
In light of these developments, the top management of ME decided to implement a quality management system (QMS) based on ISO 9001. After having an effective QMS in place for over a year, they applied for a certification audit.
A team of four auditors was appointed for the audit, including Li Na as the audit team leader. Initially, the audit team conducted a general review of ME's documents, including the quality policy, operational procedures, inventory lists, QMS scope, process documentation, training records, and previous audit reports.
Li Na stated that this would allow the team to maintain a systematic and structured approach to gathering documents for all audit stages. While reviewing the documented information, the team observed some minor issues but did not identify any major nonconformities. Therefore, Li Na claimed that it was not necessary to prepare a report or conduct a meeting with ME's representatives at that stage of the audit. She stated that all areas of concern would be discussed in the next phase of the audit.
Following the on-site activities and the opening meeting with ME's top management, the audit team structured an audit test plan to verify whether ME’s QMS conformed to Clause 8.2.1 (Customer Communication) of ISO 9001.
To do so, they gathered information through group interviews and sampling. Li Na conducted interviews with departmental managers in the first group and then with top management. In addition, she chose a sampling method that sufficiently represented customer complaints from both areas of ME's operations.
The team members were responsible for the sampling procedure. They selected a sample size of 4 out of 45 customer complaints received weekly for electrical services and 2 out of 10 complaints for mechanical services.
Afterward, the audit team evaluated the evidence against the audit criteria and generated the audit findings.
According to general principles of sampling procedure, did the audit team select a valid sample for electrical services?
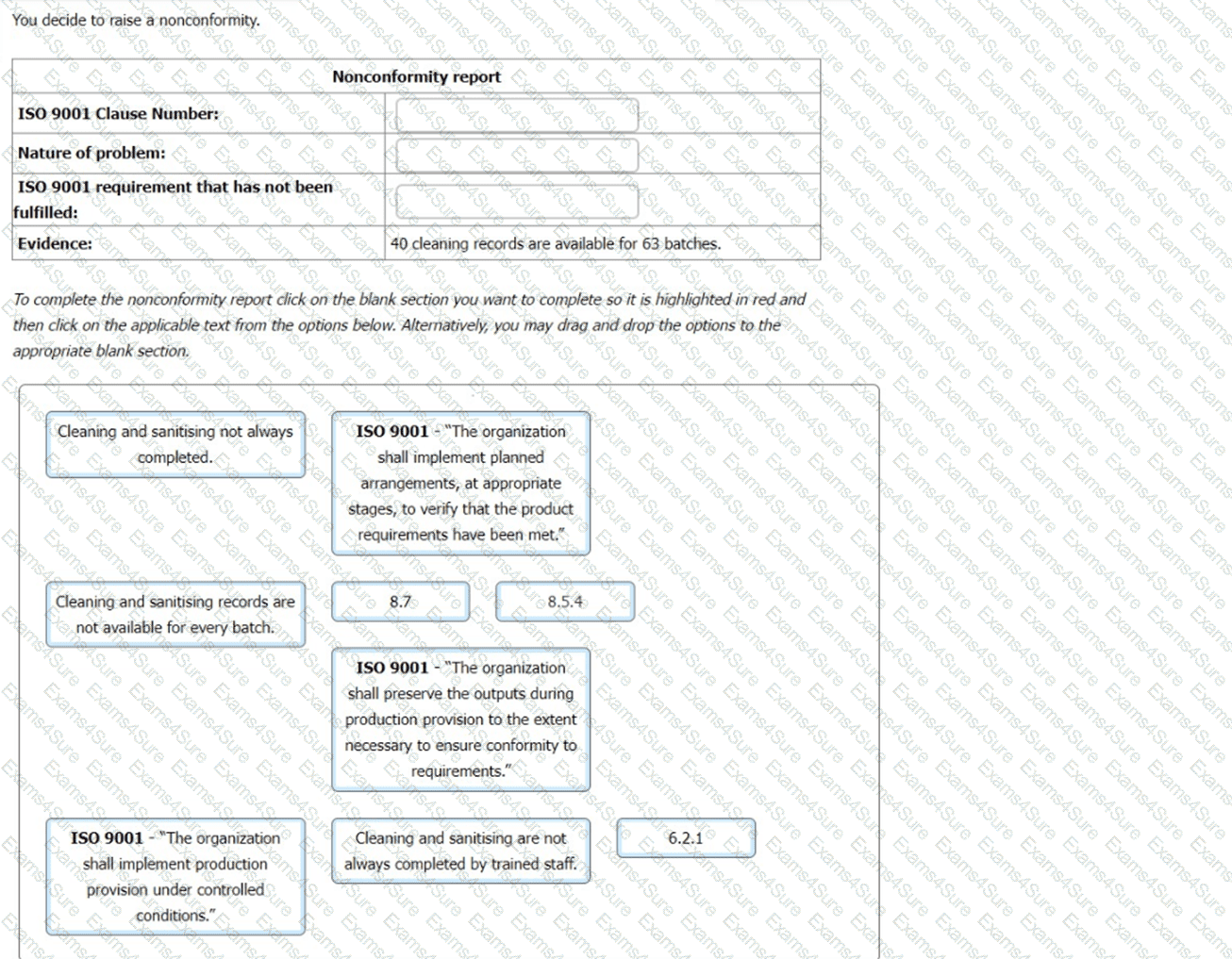
During a second-party audit, the auditor examines the records that are available for the external provider, ABC Forgings, to whom manufacturing has recently been outsourced.
There are standard external provider checklists for three competitors for the contract and there are inspection records from the trial manufacturing batches produced by ABC Forgings. There is no documented evidence of the criteria used to confirm the appointment of ABC Forgings, and no contract or terms and conditions. Ongoing monitoring indicates that external provider performance is satisfactory, but no documented information has been retained.
Select two options for the evidence which demonstrates a nonconformity with clause 8.4 of ISO 9001.
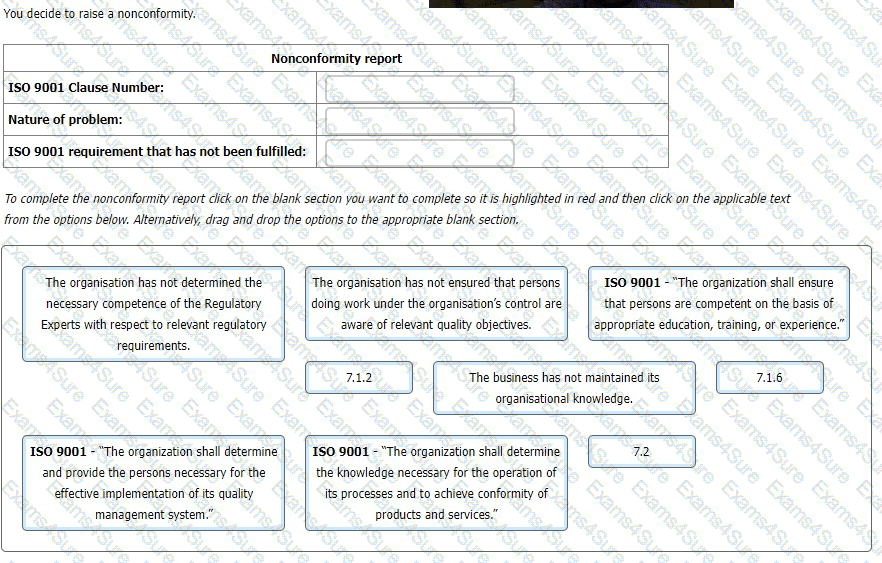
You are carrying out an audit to ISO 9001 at an organisation which offers regulatory consultancy services to manufacturers of cosmetics.
You are interviewing the Technical Director (TD), who manages a team of regulatory experts responsible for providing regulatory services to customers.
You: "How do you ensure your regulatory team's competence concerning regulatory requirements is maintained?"
TD: "The two Regulatory Experts we employ full-time have years of experience of working in the cosmetics industry."
You: "How is their regulatory competence maintained?"
TD: "They are dedicated individuals with lots of contacts in the sector."
You: "How does the business enable them to maintain their understanding of current regulatory requirements?"
TD: "We leave that up to them."
Scenario 2:
Bell is a Canadian food manufacturing company that operates globally. Their main products include nuts, dried fruits, and confections. Bell has always prioritized product quality and has maintained a good reputation for many years. However, the company's production error rate increased significantly, leading to more customer complaints.
To increase efficiency and customer satisfaction, Bell implemented a Quality Management System (QMS) based on ISO 9001. The top management established a QMS implementation team comprising five middle managers from various departments, including Leslie, the quality manager.
Leslie was responsible for assigning responsibilities and authorities for QMS-related roles. He also suggested including a top management representative in the QMS team, but top management declined due to other priorities.
The team defined the QMS scope as:
"The scope of the QMS includes all activities related to food processing."
Leslie established a quality policy and presented it to the team for review before top management approval. Top management also proposed a new strategy for handling customer complaints, requiring biweekly customer surveys to monitor customer perceptions.
The quality policy was established by Leslie and approved by top management. Is this acceptable? Please refer to scenario 2.
According to the ISO 9001 standard, which one of the following is a defined responsibility of top management?
Which one of the following options is the definition of the context of an organisation?


TESTED 04 Apr 2025
Hi this is Romona Kearns from Holland and I would like to tell you that I passed my exam with the use of exams4sure dumps. I got same questions in my exam that I prepared from your test engine software. I will recommend your site to all my friends for sure.
Our all material is important and it will be handy for you. If you have short time for exam so, we are sure with the use of it you will pass it easily with good marks. If you will not pass so, you could feel free to claim your refund. We will give 100% money back guarantee if our customers will not satisfy with our products.