HCIP-Datacom-Advanced Routing & Switching Technology V1.0
Last Update 16 hours ago
Total Questions : 156
HCIP-Datacom-Advanced Routing & Switching Technology V1.0 is stable now with all latest exam questions are added 16 hours ago. Incorporating H12-831_V1.0 practice exam questions into your study plan is more than just a preparation strategy.
H12-831_V1.0 exam questions often include scenarios and problem-solving exercises that mirror real-world challenges. Working through H12-831_V1.0 dumps allows you to practice pacing yourself, ensuring that you can complete all HCIP-Datacom-Advanced Routing & Switching Technology V1.0 practice test within the allotted time frame.
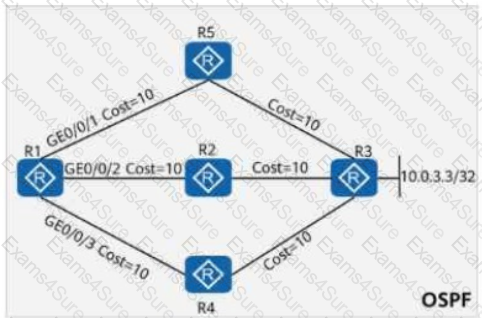
On the OSPF network shown in the figure, the cost values of links are marked. OSPF IP FRR is enabled on R1, and the maximum load-balancing 8 command is configured in the OSPF process. If a service passes through the path R1 → R5 → R3 to reach 10.0.3.3/32, which of the following is the backup outbound interface for the service?
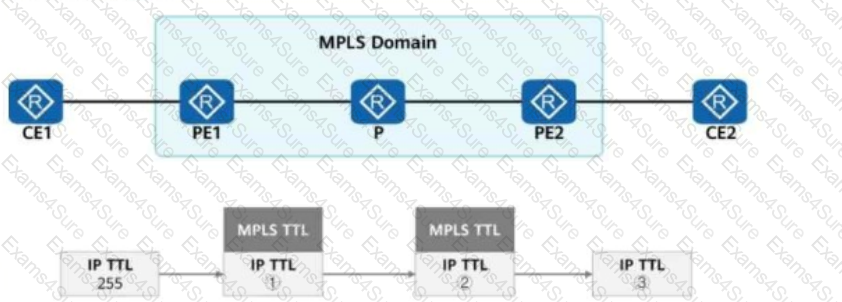
When an IP packet passes through an MPLS network, an MPLS device processes the TTL value in the packet.
If the pipe mode is used in the topology shown in the figure, which of the following is the TTL value in the IP packet?
Options:
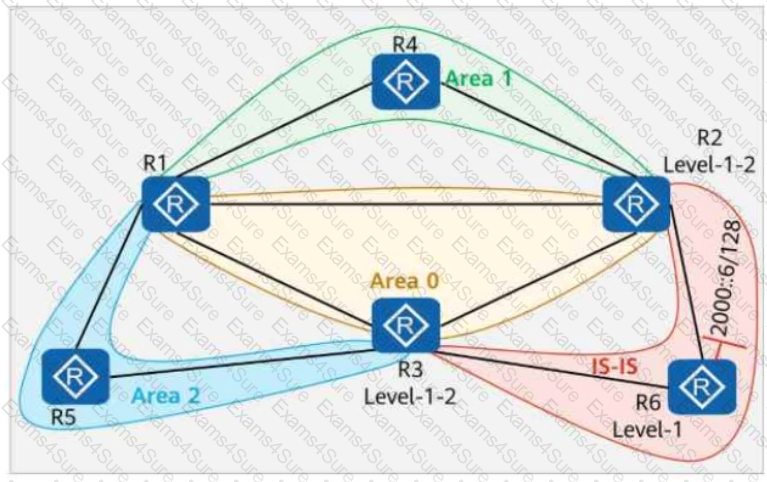
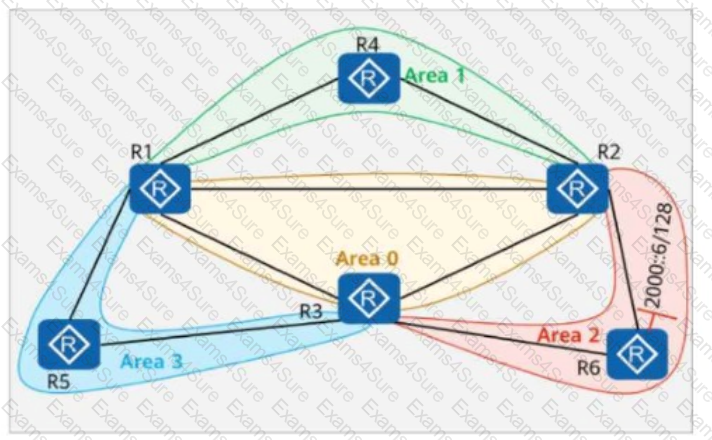
On the network shown in the figure, IS-IS IPv6 runs on R2, R6, and R3, and the IPv6 address of Loopback0 on R6 is 2000::6/128. OSPFv3 runs on other links. Area 1 is a stub area, and Area 2 is an NSSA. IS-IS routes are imported to OSPFv3 on R2 and R3. Which of the following statements are true?
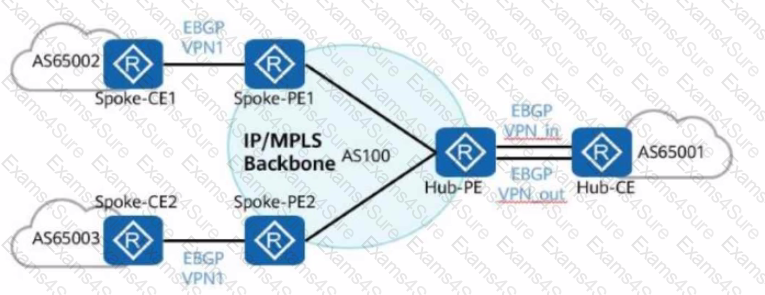
In the hub-spoke networking shown in the figure, the Hub-PE can be configured to allow repetitive local AS numbers for correct route transmission.
On the IS-IS IPv6 network shown in the figure:
Multi-topology is enabled on all routers.
The IPv6 address of Loopback0 on R4 is 2000::4/128.
The command ipv6 summary 2000::/64 level-2 is configured in the IS-IS processes of R2 and R1.
The command ipv6 import-route isis level-2 into level-1 is configured in the IS-IS processes of R1, R2, and R3.
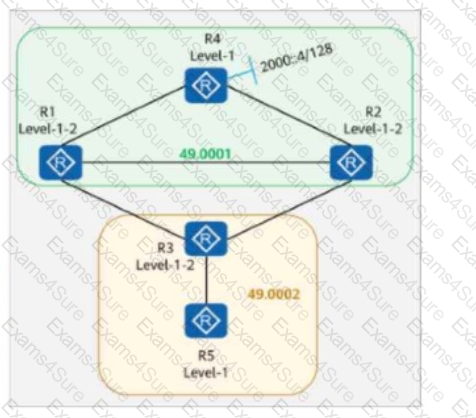
Which of the following routers have the route 2000::/64 in their routing tables?
On the OSPFv3 network shown in the figure:
Area 1 is a stub area, Area 2 is a common area, and Area 3 is an NSSA (Not-So-Stubby Area).
The IPv6 address of Loopback0 on R6 is 2000::6/128.
The router ID of each router is 10.0.X.X, where X is the router number.
The stub no-summary command is configured in Area 1 on R2.
Which of the following statements is true?
A network engineer provides a troubleshooting report after rectifying a fault. The actual network is simplified into the one shown in the figure, where R1 and R2 both have OSPF enabled and function as the gateways of PC1 and PC2, respectively.
Given this, which of the following statements are true?
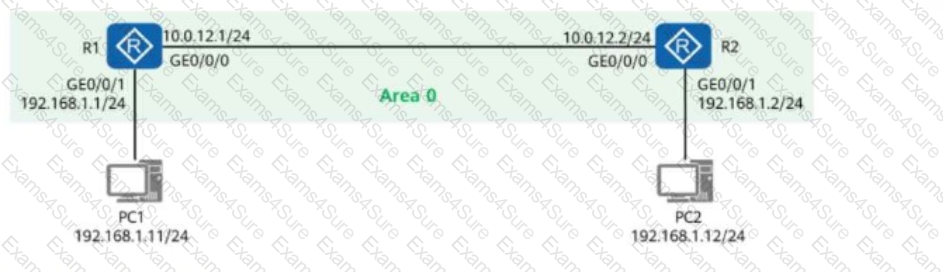
Network Topology:
R1:
Interface GE0/0/0: 10.0.12.1/24 (Connected to R2)
Interface GE0/0/1: 192.168.1.1/24 (Gateway for PC1)
R2:
Interface GE0/0/0: 10.0.12.2/24 (Connected to R1)
Interface GE0/0/1: 192.168.1.2/24 (Gateway for PC2)
Options:
On a PIM-SM multicast network, a network engineer finds that multicast clients cannot receive multicast data. Which of the following is not a possible cause of this problem?
On the network shown in the figure, the network administrator configures the DHCP snooping trust function on the switch.
GE0/0/2 is a trusted interface (connected to the DHCP Server).
GE0/0/3 is an untrusted interface (potential attacker).
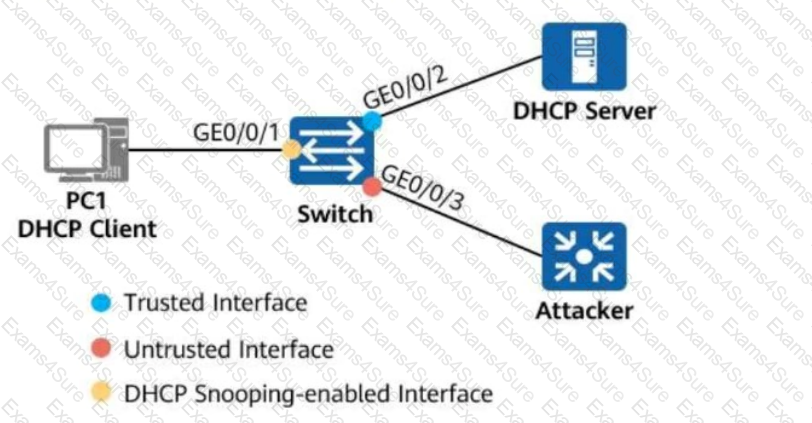
Which of the following statements are true about the two interfaces?
Options:


TESTED 04 Apr 2025
Hi this is Romona Kearns from Holland and I would like to tell you that I passed my exam with the use of exams4sure dumps. I got same questions in my exam that I prepared from your test engine software. I will recommend your site to all my friends for sure.
Our all material is important and it will be handy for you. If you have short time for exam so, we are sure with the use of it you will pass it easily with good marks. If you will not pass so, you could feel free to claim your refund. We will give 100% money back guarantee if our customers will not satisfy with our products.