Nokia IS-IS Routing Protocol
Last Update 1 month ago
Total Questions : 40
Nokia IS-IS Routing Protocol is stable now with all latest exam questions are added 1 month ago. Incorporating 4A0-112 practice exam questions into your study plan is more than just a preparation strategy.
4A0-112 exam questions often include scenarios and problem-solving exercises that mirror real-world challenges. Working through 4A0-112 dumps allows you to practice pacing yourself, ensuring that you can complete all Nokia IS-IS Routing Protocol practice test within the allotted time frame.
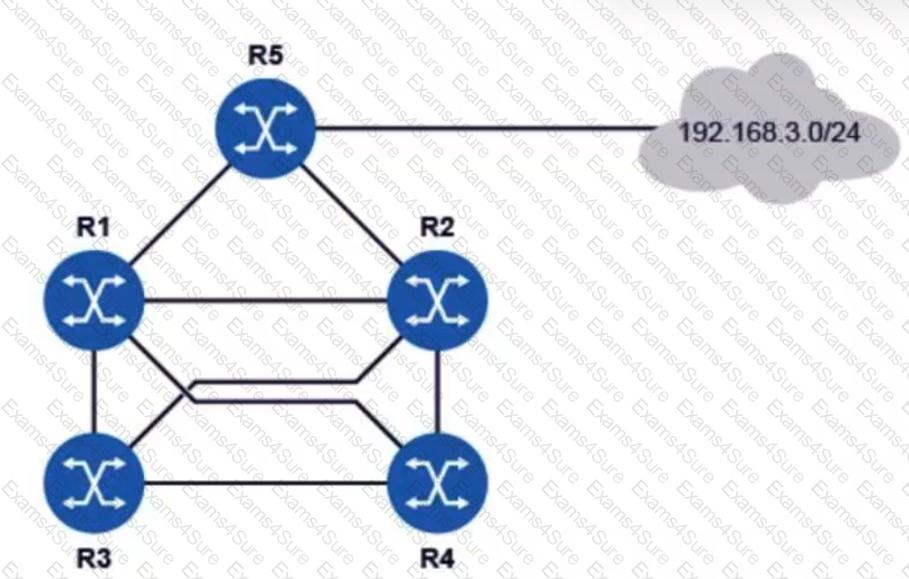
All routers in the diagram are running an interior gateway protocol (IGP) and have been configured with an ECMP value of 4. Router R5 advertises the prefix 192.168.3.0/24 using the IGP. Assuming all links have the same cost, how many entries for prefix 192.168.3.0/24 will be in router R3’s routing table?
An IS-IS router receives a CSNP that references an older LSP than the one in its local database. What action is taken?
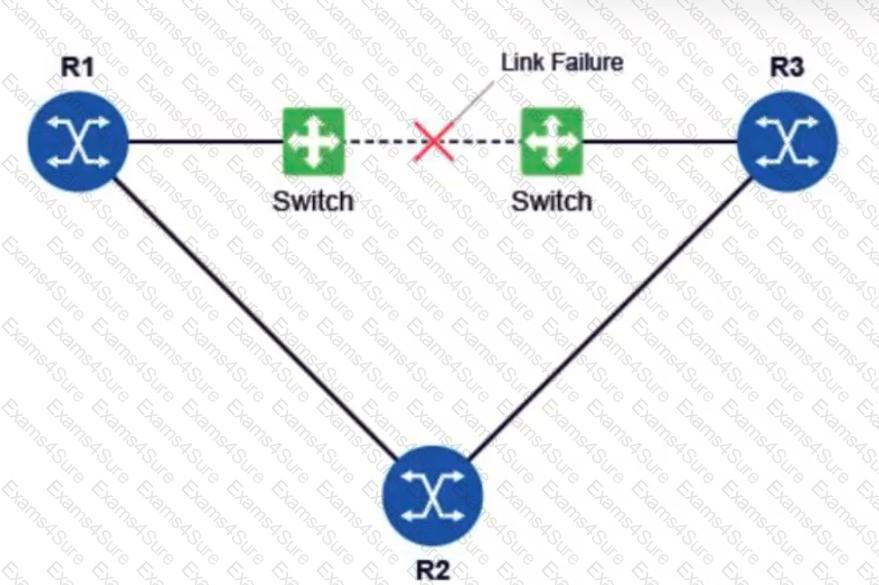
All routers in the diagram are running a link-state routing protocol. Before the link failure, all routers have operational adjacencies with each other and there is a BFD session between routers R1 and R3. After the link failure, which of the following affects the routing protocol’s convergence time?
Which of the following is a valid alternative representation of the IPv6 address
2001:0da8:0000:0000:0024:0000:4ab9:0300?
A series of actions are triggered on a router as a result of enabling both loopfree-alternate for a link-state routing protocol and ip-fast-reroute. Which of the following is NOT one of those actions?
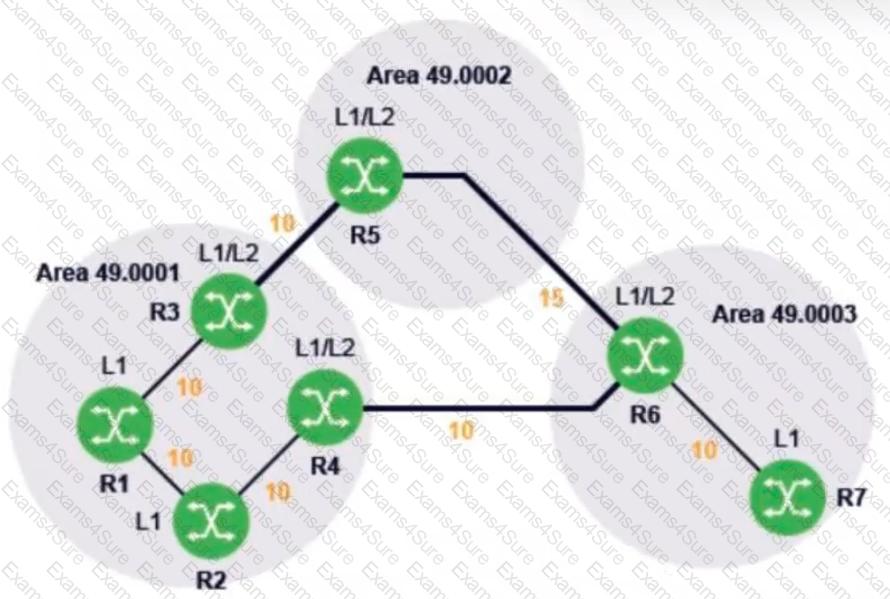
In the diagram, all routers are using IS-IS as their routing protocol. The number next to each link is its metric value.
What path will traffic follow from router R1 to router R7, and from router R7 to router R1?
A routing domain is using a single-area link-state routing protocol. Which of the following is NOT information that a router can share with other routers in the domain using protocol-specific messages?
For a link-state routing protocol, which of the following statements about link-state updates is FALSE?
Two IS-IS neighboring routers are trying to establish an adjacency, but the interface has been configured as broadcast on one of them and as point-to-point on the other. Why is the adjacency not established?


TESTED 12 Mar 2025
Hi this is Romona Kearns from Holland and I would like to tell you that I passed my exam with the use of exams4sure dumps. I got same questions in my exam that I prepared from your test engine software. I will recommend your site to all my friends for sure.
Our all material is important and it will be handy for you. If you have short time for exam so, we are sure with the use of it you will pass it easily with good marks. If you will not pass so, you could feel free to claim your refund. We will give 100% money back guarantee if our customers will not satisfy with our products.