MuleSoft Certified Integration Architect - Level 1
Last Update 1 month ago
Total Questions : 273
MuleSoft Certified Integration Architect - Level 1 is stable now with all latest exam questions are added 1 month ago. Incorporating MCIA-Level-1 practice exam questions into your study plan is more than just a preparation strategy.
MCIA-Level-1 exam questions often include scenarios and problem-solving exercises that mirror real-world challenges. Working through MCIA-Level-1 dumps allows you to practice pacing yourself, ensuring that you can complete all MuleSoft Certified Integration Architect - Level 1 practice test within the allotted time frame.
Refer to the exhibit.
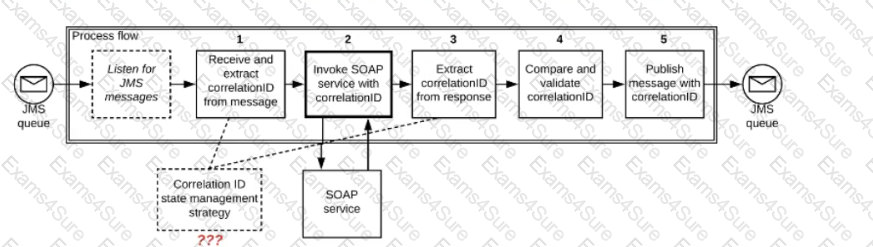
A Mule application is deployed to a multi-node Mule runtime cluster. The Mule application uses the competing consumer pattern among its cluster replicas to receive JMS messages from a JMS queue. To process each received JMS message, the following steps are performed in a flow:
Step l: The JMS Correlation ID header is read from the received JMS message.
Step 2: The Mule application invokes an idempotent SOAP webservice over HTTPS, passing the JMS Correlation ID as one parameter in the SOAP request.
Step 3: The response from the SOAP webservice also returns the same JMS Correlation I
D.
Step 4: The JMS Correlation ID received from the SOAP webservice is validated to be identical to the JMS Correlation ID received in Step 1.
Step 5: The Mule application creates a response JMS message, setting the JMS Correlation ID message header to the validated JMS Correlation ID and publishes that message to a response JMS queue.
Where should the Mule application store the JMS Correlation ID values received in Step 1 and Step 3 so that the validation in Step 4 can be performed, while also making the overall Mule application highly available, fault-tolerant, performant, and maintainable?
What approach configures an API gateway to hide sensitive data exchanged between API consumers and API implementations, but can convert tokenized fields back to their original value for other API requests or responses, without having to recode the API implementations?
A platform architect includes both an API gateway and a service mesh in the architect of a distributed application for communication management.
Which type of communication management does a service mesh typically perform in this architecture?
An organization has deployed both Mule and non-Mule API implementations to integrate its customer and order management systems. All the APIs are available to REST clients on the public internet.
The organization wants to monitor these APIs by running health checks: for example, to determine if an API can properly accept and process requests. The organization does not have subscriptions to any external monitoring tools and also does not want to extend its IT footprint.
What Anypoint Platform feature provides the most idiomatic (used for its intended purpose) way to monitor the availability of both the Mule and the non-Mule API implementations?
An organization is building a test suite for their applications using m-unit. The integration architect has recommended using test recorder in studio to record the processing flows and then configure unit tests based on the capture events
What are the two considerations that must be kept in mind while using test recorder
(Choose two answers)
A company is using Mulesoft to develop API's and deploy them to Cloudhub and on premises targets. Recently it has decided to enable Runtime Fabric deployment option as well and infrastructure is set up for this option.
What can be used to deploy Runtime Fabric?
What metrics about API invocations are available for visualization in custom charts using Anypoint Analytics?
Refer to the exhibit.
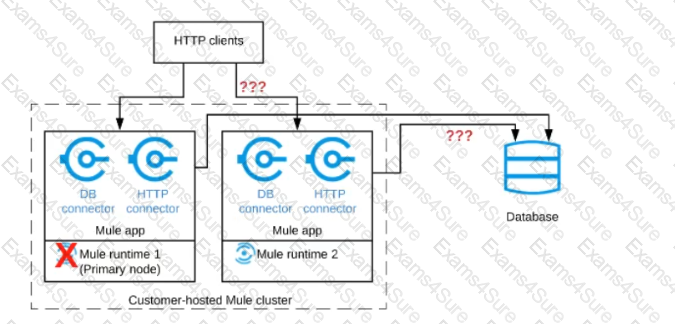
A Mule application is deployed to a cluster of two customer-hosted Mute runtimes. The Mute application has a flow that polls a database and another flow with an HTTP Listener.
HTTP clients send HTTP requests directly to individual cluster nodes.
What happens to database polling and HTTP request handling in the time after the primary (master) node of the cluster has railed, but before that node is restarted?
What is true about the network connections when a Mule application uses a JMS connector to interact with a JMS provider (message broker)?
A global, high-volume shopping Mule application is being built and will be deployed to CloudHub. To improve performance, the Mule application uses a Cache scope that maintains cache state in a CloudHub object store. Web clients will access the Mule application over HTTP from all around the world, with peak volume coinciding with business hours in the web client's geographic location. To achieve optimal performance, what Anypoint Platform region should be chosen for the CloudHub object store?


TESTED 12 Mar 2025
Hi this is Romona Kearns from Holland and I would like to tell you that I passed my exam with the use of exams4sure dumps. I got same questions in my exam that I prepared from your test engine software. I will recommend your site to all my friends for sure.
Our all material is important and it will be handy for you. If you have short time for exam so, we are sure with the use of it you will pass it easily with good marks. If you will not pass so, you could feel free to claim your refund. We will give 100% money back guarantee if our customers will not satisfy with our products.